Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣是一岁以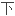
 婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
 主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
 原因。
原因。
 ]软化,喉软
]软化,喉软 软化病
软化病Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣是一岁以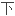
 婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
 主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
 原因。
原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是婴儿期最常
 非传染性喘鸣
非传染性喘鸣 病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常
病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常
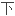
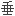 。
。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件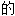 观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.

 喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼
喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼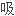 窘迫常
窘迫常 的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是婴儿期最常 的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,
的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,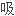
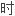 声门上有异常的下垂。
声门上有异常的下垂。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
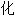 ,喉软骨软
,喉软骨软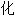
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫
 的主诉,而喉头软
的主诉,而喉头软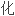 症是最
症是最
 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软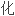 是婴儿期最
是婴儿期最
 的非传染性喘鸣的
的非传染性喘鸣的 因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有
因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有
 的下垂。
的下垂。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
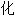 ,喉软骨软
,喉软骨软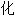 病
病Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣 一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常 的主诉,而喉
的主诉,而喉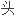 软
软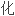 症
症 最常
最常 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软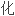
 婴儿期最常
婴儿期最常 的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常的下垂。
的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常的下垂。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣是一岁以下 婴幼儿呼吸窘
婴幼儿呼吸窘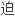


 主诉,而喉头软化症是最
主诉,而喉头软化症是最

 原因。
原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是婴儿期最


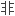 传染性喘鸣
传染性喘鸣 病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异
病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异
 下垂。
下垂。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件 观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要
 是一岁以下
是一岁以下
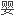
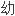
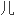 呼吸窘迫常
呼吸窘迫常
 主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
 原因。
原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是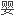
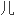 期最常
期最常
 非传染性
非传染性

 病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常
病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门上有异常 下垂。
下垂。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件 观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
 要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常 的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是婴儿期最常 的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸
的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸
 门上有异常的下垂。
门上有异常的下垂。
 明:以上例
明:以上例 、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 [软
[软 ]软化,
]软化, 软
软 软化病
软化病Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
摘要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常 的主诉,而
的主诉,而 头软化症是最常
头软化症是最常 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
 软化是婴儿期最常
软化是婴儿期最常 的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门
的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸气时声门 有异常的下垂。
有异常的下垂。
声明:以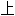

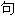 、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
Although laryngomalacia is the leading cause of stridor in infancy, vocal cord paralysis, despite its low incidence, is still the second most common cause.
 要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常
要喘鸣是一岁以下的婴幼儿呼吸窘迫常 的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常
的主诉,而喉头软化症是最常 的原因。
的原因。
Laryngomalacia is the most common etiology of non-infectious molluscum in infancy.Endoscopic morphology revealed abnormal droop of sub-glottis structures in inhale.
喉软化是婴儿期最常 的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸
的非传染性喘鸣的病因,内镜检查显示,吸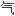
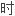
 门上有异常的下垂。
门上有异常的下垂。
 明:以上例
明:以上例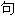 、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。